Register now and start:
- Accessing PAR Training
- Shopping PAR products & tools
- Using online assessments with PARiConnect
The FAR is a comprehensive assessment of reading and related processes. It is unique in that it helps you determine the examinee's specific subtype of dyslexia to inform decisions about appropriate interventions.
Choose to administer the full battery or, for a shorter administration time, only the subtests associated with an individual reading index, or individual subtests.
FAR author, Dr. Steven Feifer, explains what the Feifer Assessment of Reading offers that other tests for dyslexia do not, and why it is not just another reading test.
Listen as he articulates that the FAR is a diagnostic achievement test that doesn't simply give you a student's reading level, but tells you why the student is at that level, which leads to better intervention selection.
FAR author, Dr. Steven Feifer, explains what the Feifer Assessment of Reading offers that other tests for dyslexia do not, and why it is not just another reading test. He shares that the FAR is a diagnostic achievement test that doesn't simply give you a student's reading level, but tells you WHY the student is at that level, which leads to better intervention selection.The FAR offers a broad assessment of reading that includes more than dyslexia.
Hear from Dr. Steven Feifer about how this approach to reading assessment presents a more detailed view of where your student may be struggling.
The FAR is based on the theory of reading and evaluating multiple pathways of reading is one way the it provides more accurate test results.
Watch as Dr. Steven Feifer explains how the FAR combines neuroscience and education to test for the primary processing components of reading.
The FAR™ is based on cognitive processes in the brain, a neurodevelopmental approach to reading which best answers the why a student struggles with reading, which helps practitioners figure out how to treat it.
Hear Dr. Steven Feifer talk about the importance of the neurodevelopmental approach when you test for dyslexia and other reading disorders. He discusses how the FAR™ investigates all pathways in the brain that contribute to reading and comprehension to help you better understand what is hindering your student from learning.
PARiConnect helps streamline the administration, scoring, and report generation of the FAR.
In this video, Dr. Steven Feifer highlights PARiConnect features that will simplify and improve your assessment by providing an instant and custom 25-page interpretive report.
"It only takes about 3 minutes to take the raw scores, add them up and transfer into PARiConnect. Instantly, you can choose from several reports: interpretive, comprehensive score, and reliable change. If you are craving practical strategies that you can start tomorrow to help improve your student's reading skills, I encourage you to administer the FAR."
- Steven G. Feifer, DEd
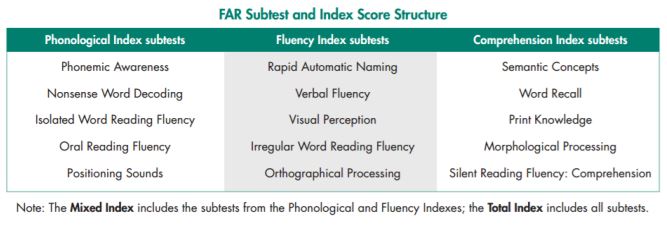
Most reading assessments contain 3-4 subtests, the FAR is a diagnostic reading test, therefore it has 15.
Hear Dr. Steven Feifer walk through the importance of the 15 subtest topics, and how they enable you to do more for your students.
Watch as Dr. Steven Feifer shares how the FAR™ can reliably monitor your student’s progress and measure how your chosen intervention has affected their scores. He explains that it does this through the Reliable Change Index, and it is just one more way the FAR™ stands out from other reading tests.
Hear Dr. Steven Feifer explain how the FAR tests beyond just reading ability to reveal why your student is struggling with reading.
According to the Interactive Dynamic Literacy (IDL) Model, yes they are. While there are unique processes and skills in reading and writing, largely these skills have shared processes. According to the IDL a student with dyslexia can also have written composition difficulties. Also, executive functions such as working memory and attention can play a part in both reading and writing.
Listen as Dr. Steven Feifer discusses why the FAR and FAW work perfectly together when you have a referral for a language-based learning disability. They are both based on neuropsychological theory, seek to address processing issues and can be used to help diagnose dyslexia and executive functioning issues. Find out where weaknesses are in writing and reading and then review the prescriptive interventions recommended for the best path forward. He explains how the FAR looks at four subtypes of reading disorders while the FAW looks at three subtypes of written language disorders.
When the FAW, FAR, and FAM are used together, you get valuable information in less time that allows you to more holistically assess your students for reading, writing, and math disorders. Based on a neuropsychological theory of reading, writing, and math, the Feifer family of products reveals the root of your student's struggles and generates interpretive reports to aid in your intervention decision making. Hear more from test author Dr. Steve Feifer in this video.
Teachers, parents, and students want more than what competing tests of reading, writing, and math offer. The Feifer family of products is designed to work together to get to the heart of the struggle and answer why a student is struggling with learning. Learn about the advantages of integrating the FAR, FAM, and FAW into your practice from test author Dr. Feifer in this video.
Hear test author Dr. Steven Feifer discuss what sets the FAR apart and how this assessment tool can help you create targeted interventions that support your students’ individual needs.
Why should you choose to use the Feifer Assessment of Reading in your assessments for dyslexia? Find out in this video, where test author Dr. Steven Feifer covers the key reasons.
It only takes about 3 minutes to take the raw scores, add them up and transfer into PARiConnect. Instantly, you can choose from several reports: interpretive, comprehensive score, and reliable change. If you are craving practical strategies that you can start tomorrow to help improve your student's reading skills, I encourage you to administer the FAR.
- Steven G. Feifer, DEd
According to the Interactive Dynamic Literacy (IDL) Model, yes they do. While there are unique processes and skills in reading and writing, largely these skills have shared processes. According to the IDL a student with dyslexia can also have written composition difficulties. Also, executive functions such as working memory and attention can play a part in both reading and writing. The FAR and FAW work perfectly together when you have a referral for a language-based learning disability. They both are based on neuropsychological theory, seek to address processing issues and can be used to help diagnose dyslexia and executive functioning issues. Find out where weaknesses are in writing and reading and then review prescriptive interventions recommended for the best path forward.
The FAR as it measures four subtypes of reading disorders: Phonological dyslexia, surface dyslexia, mixed dyslexia, and comprehension issues.
When a student is struggling with a specific subject in school, understanding “why” they are struggling can make all the difference for their learning and academic success. In this video, Dr. Steven Feifer—author of the FAR, FAW, FAM, and the FACT—digs into a case study about a 4th grader named Mary. He explains that by administering the Feifer Assessment of Childhood Trauma (FACT) alongside the Feifer Assessment of Reading (FAR) and Feifer Assessment of Writing (FAW), he was able to gain a broader view of Mary’s issues on both an academic and emotional level. While the results of the FAR and FAW helped him diagnose Mary with dyslexia, the FACT provided additional insights into Mary’s comfort level in school and the causes of her anxiety. The combination of all three tests in Dr. Feifer's psychoeducational evaluation helped him develop an IEP to manage Mary's dyslexia on an academic level and accommodations that helped her feel less anxious in the classroom.